Bioactive, Human VEGFR2 Dimer, His-Avi Tag
| Product Code | CSP-25127-03 |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Verified Applications | ELISA for VEGFR2-specific antibody and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) ligand protein binding assays. |
| Suggested Applications | SPR & BLI for VEGFR2-specific antibody and VEGF-A protein binding assays. Animal immunization, RUO. |
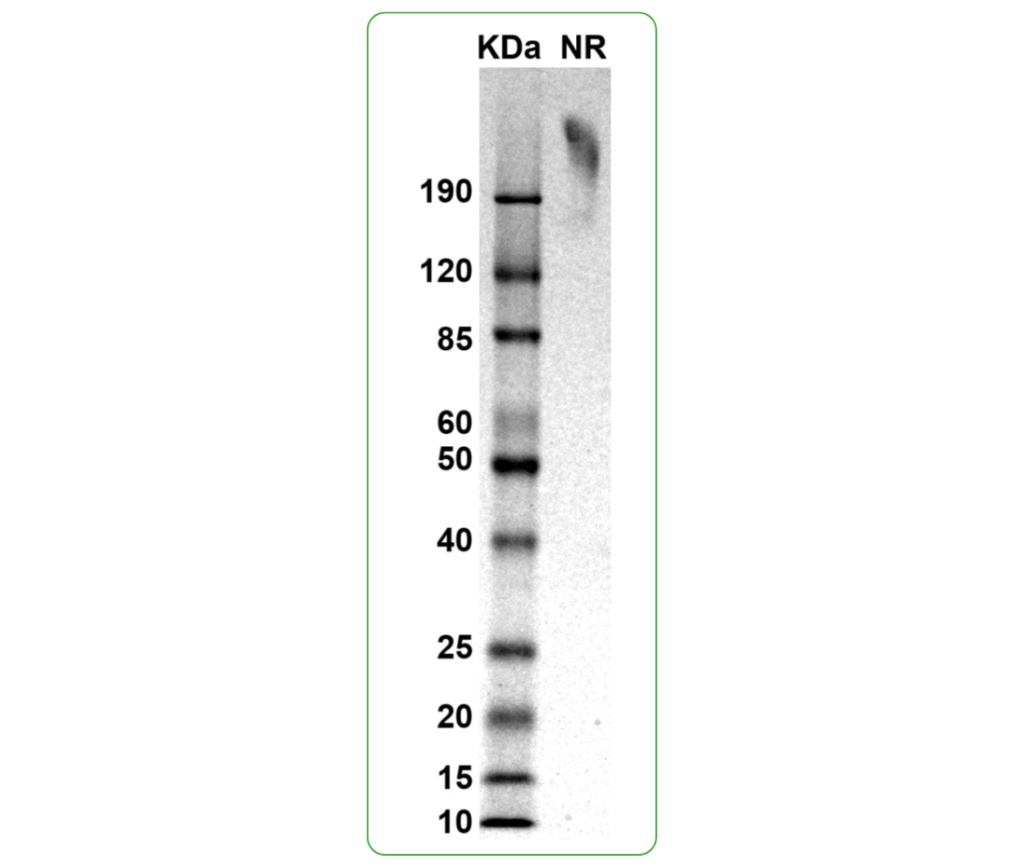
| Purity | Greater than 90% dimer form as determined by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing condition |
| Amino Acid Range | A20-E764 |
For Research Use Only (RUO)
Price: $125.00
Price: $195.00
Price: $350.00
Price: $750.00
Price: $2,500.00
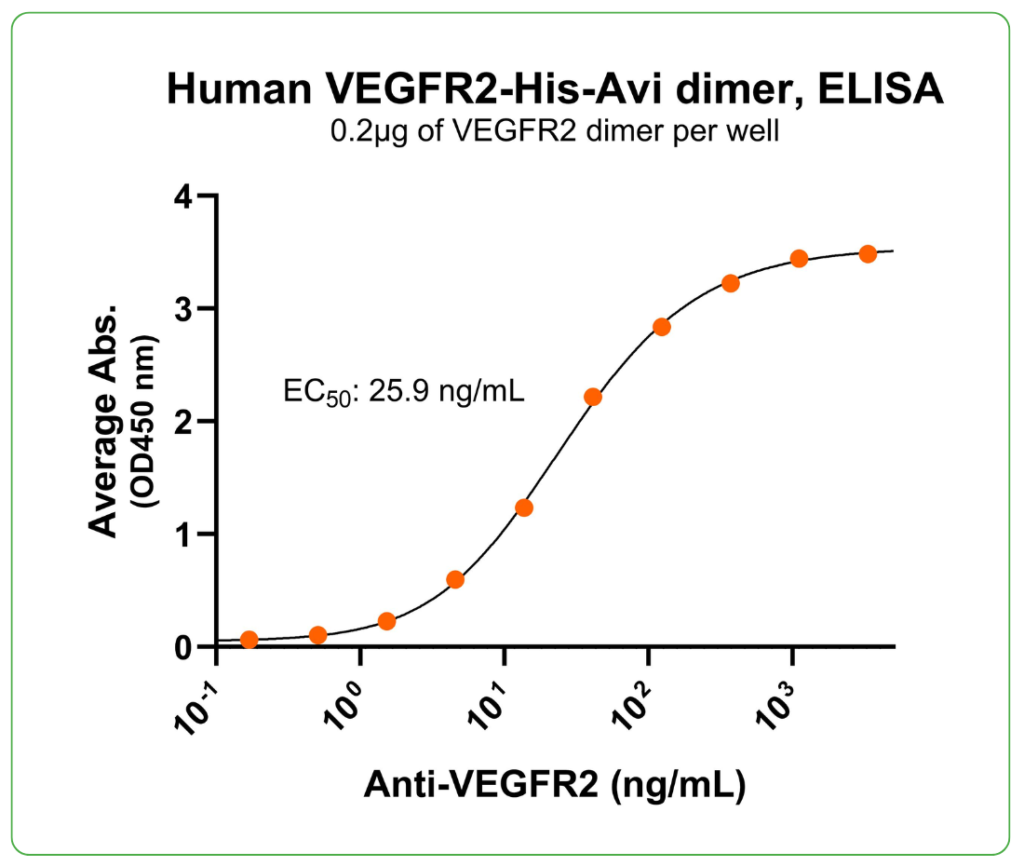
Bioactivity – Antibody Binding
Immobilized human VEGFR2-His-Avi dimer protein (CSP-25127-03) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind anti-human VEGFR2 monoclonal antibody with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 13-51.8 ng/mL (QC tested).
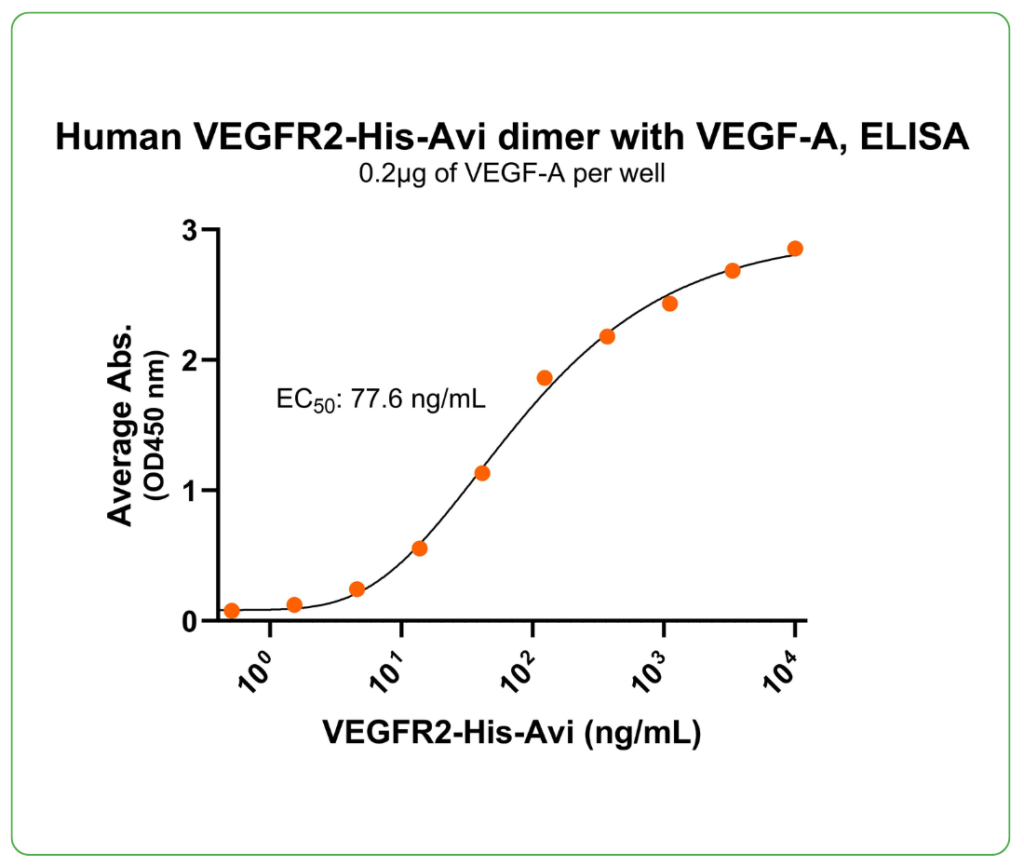
Bioactivity – Antibody Binding
Immobilized human VEGF-A 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind human VEGFR2 dimer protein, His-Avi tag (Cat. No. CSP-25127-03), with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 38.8-155.2 μg/mL (QC tested).
Specifications
Formulation: 0.22μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4
Shipping: Frozen Dry Ice
Storage: -80°C
Human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) belongs to the Type IV receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. VEGFR2 can form ligand-dependent and ligand-independent dimers. The recombinant VEGFR2 dimer protein (CSP-25127-03) is a cis-homodimer (cis-dimer) and contains a VEGFR2 extracellular domain (UniProt# P35968, amino acids Ala20-Glu764) fused with a proprietary dimer motif followed by a tandem His-Avi tag at the C-terminus. This dimeric protein is expressed in HEK293T cells. The recombinant human VEGFR2 dimer protein is bioactive and can bind to vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A). It also binds VEGFR2-specific antibodies. This VEGFR2 dimer can be used as an antigen for in vitro assays and antibody screening, and as an immunogen for immunization to generate antibodies targeting more conformational epitopes.
Protein Name: VEGFR2
UniProt #: P35968
Predicted Molecular Weight: 187 kDa
SDS PAGE Molecular Weight: The migration range of the dimer protein with glycosylation under non-reducing condition is >190 kDa on SDS PAGE.
Protein Construct: VEGFR2 dimer protein contains a VEGFR2 extracellular domain (UniProt# P35968) fused with a proprietary dimer motif followed by a tandem His-Avi tag at the C-terminus.
Background
Human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) belongs to the Type IV receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. VEGFR2 is a key receptor in the VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) signaling pathway, involved in angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels. VEGFR2 is also known as kinase insert domain receptor (KDR), cluster of differentiation 309 (CD309), and fetal liver kinase 1 (Flk1). VEGFR2, a Type I transmembrane protein, contains an extracellular domain with 7 immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) domains, a single transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain. VEGFR2 is mainly expressed on vascular endothelial cells and can bind VEGF-A and VEGF-D. VEGF binding by VEGFR2 causes it to homodimerize which is essential for it to stimulate cellular responses such as vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. In pathological conditions, ligand-independent dimerization of VEGFR2 can contribute to abnormal angiogenesis. Abnormal angiogenesis is associated with a variety of diseases such as tumor neovascularization, diabetic retinopathy, rheumatoid arthritis, and age-related macular degeneration. Abnormal angiogenesis is a major contributing factor in the growth and spread of a variety of cancers and inhibition of VEGFR2 activity offers a potential and promising approach to cancer therapy.
Alternate Names: Kinase insert domain receptor, KDR, cluster of differentiation 309, CD309, Fetal Liver Kinase 1, Flk1, VEGFR, VEGFR-2