Bioactive, Human TROP-2 Dimer, Flag-His Tag
| Product Code | CSP-24041-02 |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Verified Applications | ELISA for TROP-2-specific antibody binding assays. |
| Suggested Applications | ELISA for TROP-2-specific antibody binding assays. SPR & BLI for TROP-2-specific antibody binding assays. Animal immunization, RUO. |
| Purity | Greater than 90% dimer form as determined by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing condition |
| Amino Acid Range | His27-Thr274 |
For Research Use Only (RUO)
Price: $125.00
Price: $195.00
Price: $350.00
Price: $750.00
Price: $2,500.00
Bioactivity – Antibody Binding
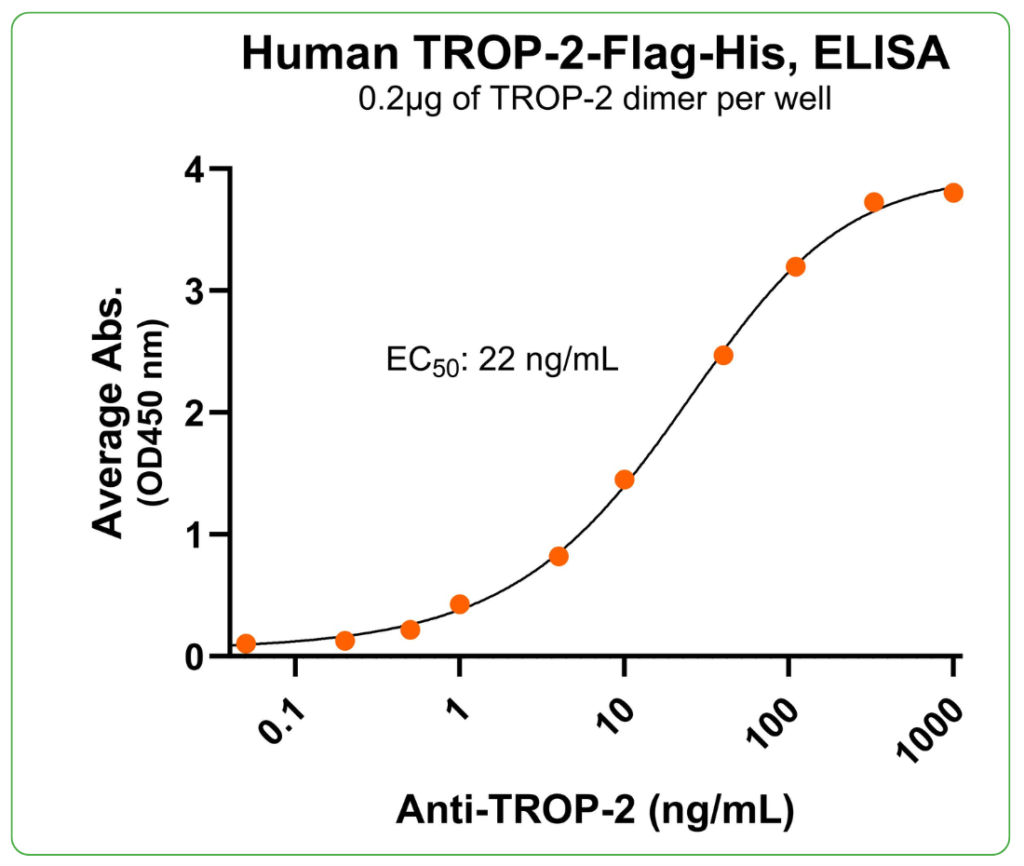
Immobilized TROP-2-Flag-His dimer protein (Cat. No. CSP-24041-02) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind anti-human TROP-2 monoclonal antibody with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 10.9-43.6 ng/mL (QC tested).
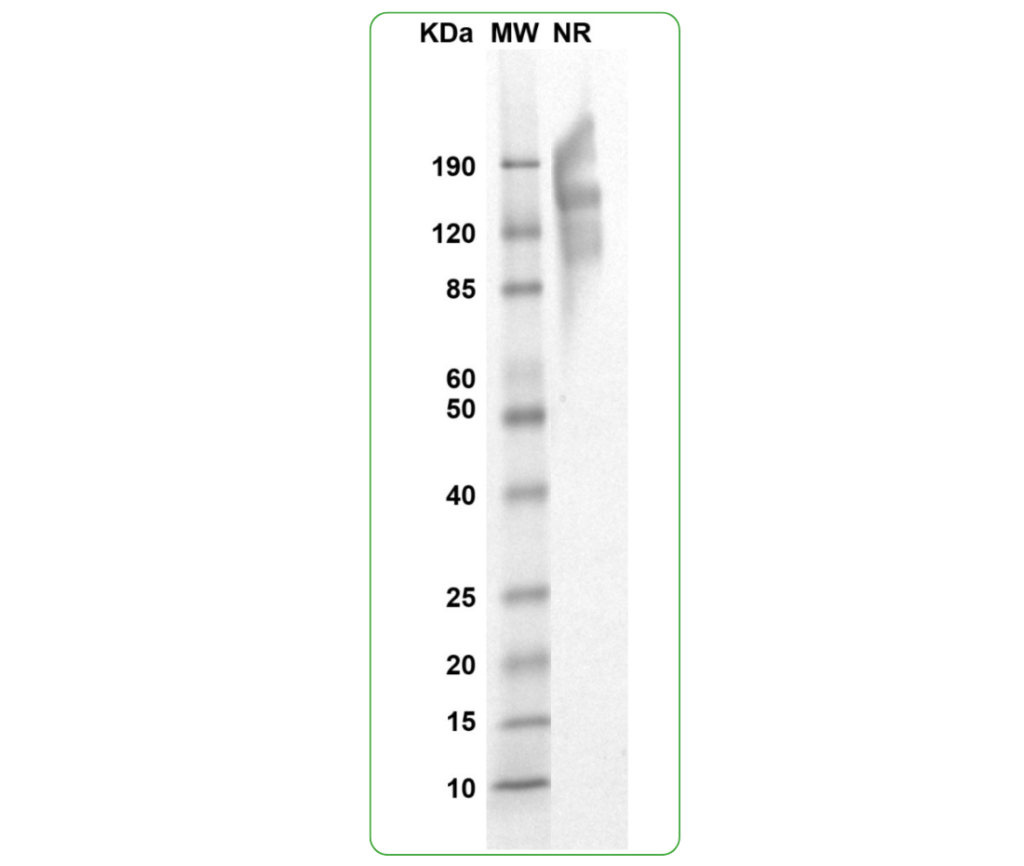
SDS-PAGE
MW: Molecular Weight marker reduced condition
NR: TROP-2 dimer under non-reducing condition
Specifications
Formulation: 0.22μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4
Shipping: Frozen Dry Ice
Storage: -80°C
Human TROP-2 (trophoblast cell surface antigen 2) is a cell-surface transmembrane type-1 glycoprotein expressed in epithelial cells of various tissues. TROP-2 exists as a monomer on the cell surface but can form dimers or oligomers on cancer cells enhancing its role in cancer progression. The recombinant TROP-2 dimer protein (TROP-2 protein dimer, CSP- 24041-02) is a cis-homodimer (cis-dimer) protein and contains a TROP-2 extracellular domain (UniProt# P09758, amino acids His27-Thr274) fused with a proprietary dimer motif followed by a tandem Flag-His tag at the C-terminus. This dimeric protein is expressed in HEK293T cells. The TROP-2 dimer protein is bioactive. It also binds TROP-2-specific antibodies. This TROP-2 dimer can be used as an antigen for in vitro assays and antibody screening, and as an immunogen for immunization to generate antibodies targeting more conformational epitopes.
Protein Name: TROP-2
UniProt #: P09758
Predicted Molecular Weight: 72 kDa
SDS PAGE Molecular Weight: The migration range of the dimer under non-reducing conditions is 90-200 kDa on SDS PAGE.
Protein Construct: TROP-2 dimer protein contains a TROP-2 extracellular domain (UniProt# P09758, amino acids His27-Thr274) fused with a dimer motif followed by a tandem Flag-His tag at the C-terminus.
Background
Human TROP-2 (trophoblast cell surface antigen 2) is a cell-surface type I transmembrane glycoprotein expressed in epithelial cells of various tissues. TROP-2 is also known as TROP2, TACSTD2, EGP-1, pancreatic carcinoma marker protein GA733–1/GA733, gastrointestinal tumor-associated antigen GA7331, GP50, M1S1, tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2, CAA1, and TTD2. TROP-2 exists as a monomer on the cell surface but can form dimers or oligomers on cancer cells enhancing its role in cancer progression. TROP-2 contains an extracellular domain, a single transmembrane helix, and a cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular domain is comprised of three subdomains: a cysteine-rich domain, a thyroglobulin type-1 domain, and a cysteine-poor domain. TROP-2 is normally involved in the maintenance of epithelial tissue integrity. It is overexpressed in many cancers including breast cancer, non-small-cell lung cancer, thyroid cancer, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, and ovarian cancer. TROP-2 overexpression is involved in cancer cell growth, proliferation, invasion, migration, and survival of cancer cells, and is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis. TROP-2 is an emerging target of cancer therapeutics..
Alternate Names: TACSTD2, epithelial glycoprotein-1, EGP-1, EGP1, GA733-1, GA7331, pancreatic carcinoma marker protein GA733–1/GA733, gastrointestinal tumor-associated antigen GA7331, GP50, membrane component chromosome 1 surface marker 1, M1S1, TROP2, tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2, tumor associated calcium signal transducer 2, trophoblast cell surface antigen 2, CAA1, TTD2
Learn more about CD4

CD4: The Glycoprotein at the Heart of Immunity, HIV Research, and Clinical Advances
CD4, or “Cluster of Differentiation 4,” is a glycoprotein expressed on CD4+ T cells and also found on the surface of other immune cells such
FAQs
What is the Function of the CD4 Glycoprotein?
The primary function of CD4 is to act as a coreceptor in the immune response. It binds to MHC class II molecules, facilitating T-cell activation and cytokine release, which are critical for immune system signaling and pathogen response. The CD4+ T-cells help initiate antibody production by B-cells and activate cytotoxic T-cells, ensuring a coordinated immune defense. Learn more on our blog about CD4 »
What is CD4 a Marker For?
CD4 serves as a surface marker for CD4+ T cells, and its levels are used to assess immune health, especially in HIV/AIDS patients. HIV specifically targets and depletes CD4+ T-cells, leading to immune system failure. CD4 counts are vital in clinical settings to monitor HIV progression and guide antiretroviral therapy decisions. Learn more on our blog about CD4 »