Recombinant Mouse PRLR Protein Dimer, His-Tag
| Product Code | CSP-25160-01 |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Verified Applications | ELISA for PRLR-specific antibody binding assays. |
| Suggested Applications | ELISA for PRLR and prolactin (PRL) ligand protein binding assays. SPR & BLI for PRLR-specific antibody and PRL protein binding assays. Animal immunization, RUO. |
| Purity | Greater than 90% dimer form as determined by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing condition |
| Amino Acid Range | Q20-D229 |
For Research Use Only (RUO)
Price: $125.00
Price: $195.00
Price: $350.00
Price: $750.00
Price: $2,500.00
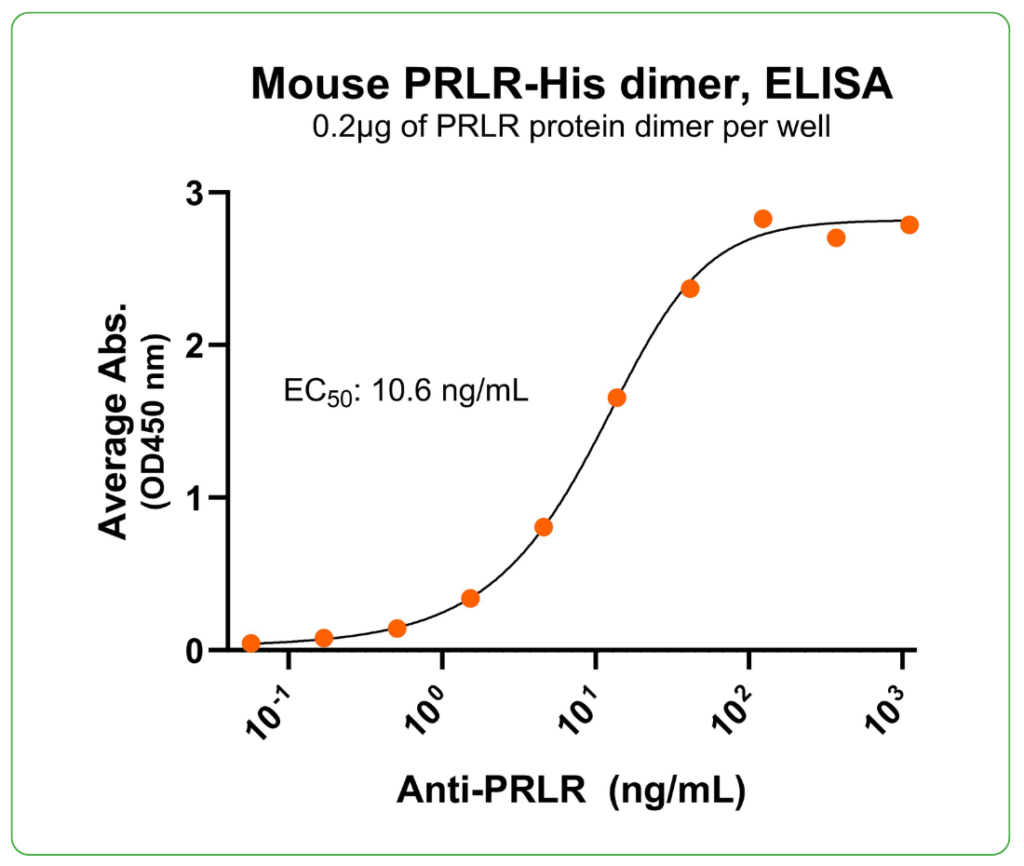
Bioactivity – Antibody Binding
Immobilized mouse PRLR protein dimer, His-tag (CSP-25160-01) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind anti-mouse PRLR monoclonal antibody with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 5.3-21.2 ng/mL (QC tested).
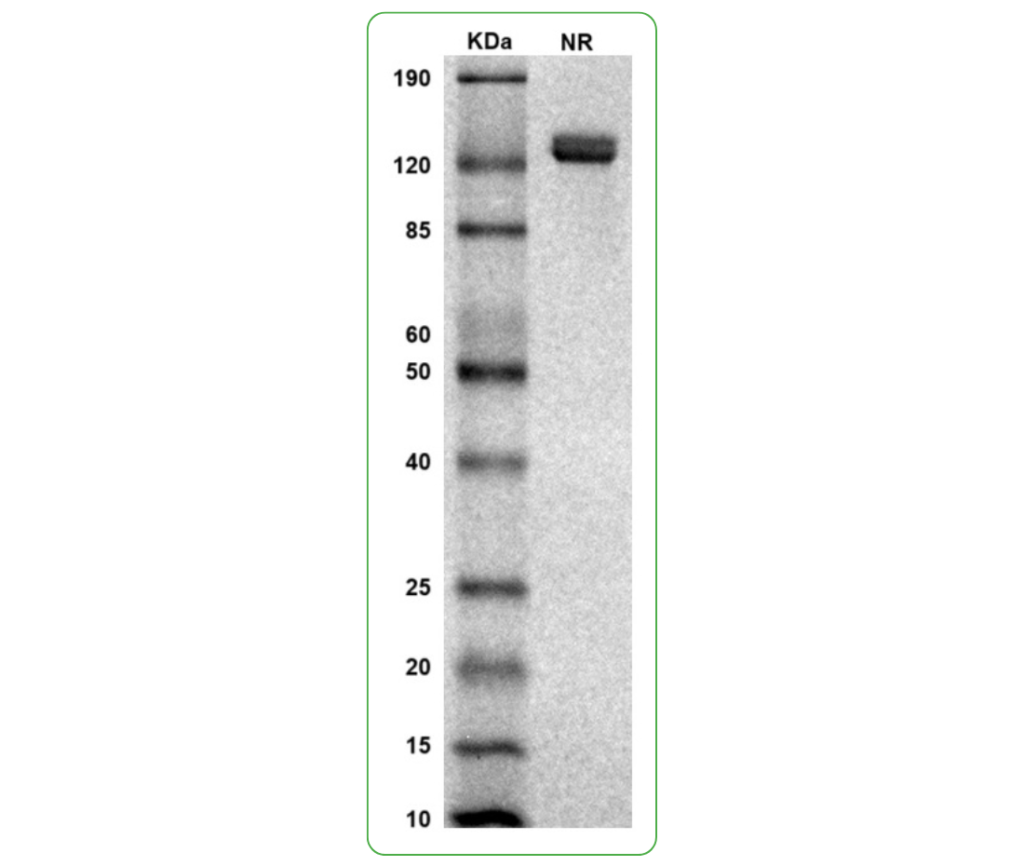
SDS-PAGE
MW: Molecular Weight marker reduced condition
NR: PRLR dimer under non-reduced condition
Specifications
Formulation: 0.22μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4
Shipping: Frozen Dry Ice
Storage: -80°C
Prolactin receptor (PRLR), also known as PRL-R, is a class 1 cytokine receptor glycoprotein that binds prolactin (PRL). PRLR contains an extracellular domain with a cytokine homology module formed by two fibronectin type III domains, D1 and D2, followed by a transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic domain. PRLR is expressed on cells in mammary glands, pituitary gland, and other tissues. PRLR exists as a monomer and can form dimers. PRLR dimerization is a critical mechanism in PRL signaling, influencing numerous physiological and pathological processes. PRLR pathological dimerization, including constitutive or ligand-independent PRLR dimers sustain abnormal signaling, contributes to cancer, hyperprolactinemia, and immune dysfunction. Dysregulation of PRLR can promote tumor activity and positively regulate the proliferation of malignant cells in breast cancer. PRLR is an attractive therapeutic target for PRLR related diseases including breast cancer, hyperprolactinemia, and metabolic disorders. While structurally and functionally similar to human PRLR, mouse PRLR is a species-specific tool essential for preclinical studies, basic research, and translational research in cancer immunotherapy.
Protein Name: PRLR
UniProt #: Q08501
Predicted Molecular Weight: 65 kDa
SDS PAGE Molecular Weight: The migration range of the dimer protein with glycosylation under non-reduced condition is between 120 and 190 kDa on SDS PAGE.
Protein Construct: Mouse PRLR protein dimer contains a PRLR extracellular domain (UniProt# Q08501) fused with a proprietary cis-dimer motif followed by a His tag at the C-terminus.
Background
Prolactin receptor (PRLR), also known as PRL-R, is a class 1 cytokine receptor glycoprotein that binds prolactin (PRL). PRLR contains an extracellular domain with a cytokine homology module formed by two fibronectin type III domains, D1 and D2, followed by a transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic domain. PRLR is expressed on cells in mammary glands, pituitary gland, and other tissues. PRLR exists as a monomer and can form dimers. PRLR dimerization is a critical mechanism in PRL signaling, influencing numerous physiological and pathological processes. PRLR pathological dimerization, including constitutive or ligand-independent PRLR dimers sustain abnormal signaling, contributes to cancer, hyperprolactinemia, and immune dysfunction. Dysregulation of PRLR can promote tumor activity and positively regulate the proliferation of malignant cells in breast cancer. PRLR is an attractive therapeutic target for PRLR related diseases including breast cancer, hyperprolactinemia, and metabolic disorders. While structurally and functionally similar to human PRLR, mouse PRLR is a species-specific tool essential for preclinical studies, basic research, and translational research in cancer immunotherapy.
Alternate Names: prolactin R, PRL-R