Bioactive, Human IFN-alpha/beta receptor R1/R2 Heterodimer, His Tag
| Product Code | CSP-24025-A1B1 |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Verified Applications | ELISA, SPR, and BLI for IFNAR-specific antibody assays; ELISA, SPR, and BLI for type I interferon (IFN) cytokine ligand/receptor protein binding assays. |
| Suggested Applications | ELISA for IFNAR-specific antibody binding assays; ELISA for type I interferon (IFN) cytokine ligand/receptor protein binding assays. SPR & BLI for IFNAR-specific antibody binding assays; SPR & BLI for type I interferon (IFN) cytokine ligand/receptor protein binding assays. Animal immunization, RUO. |
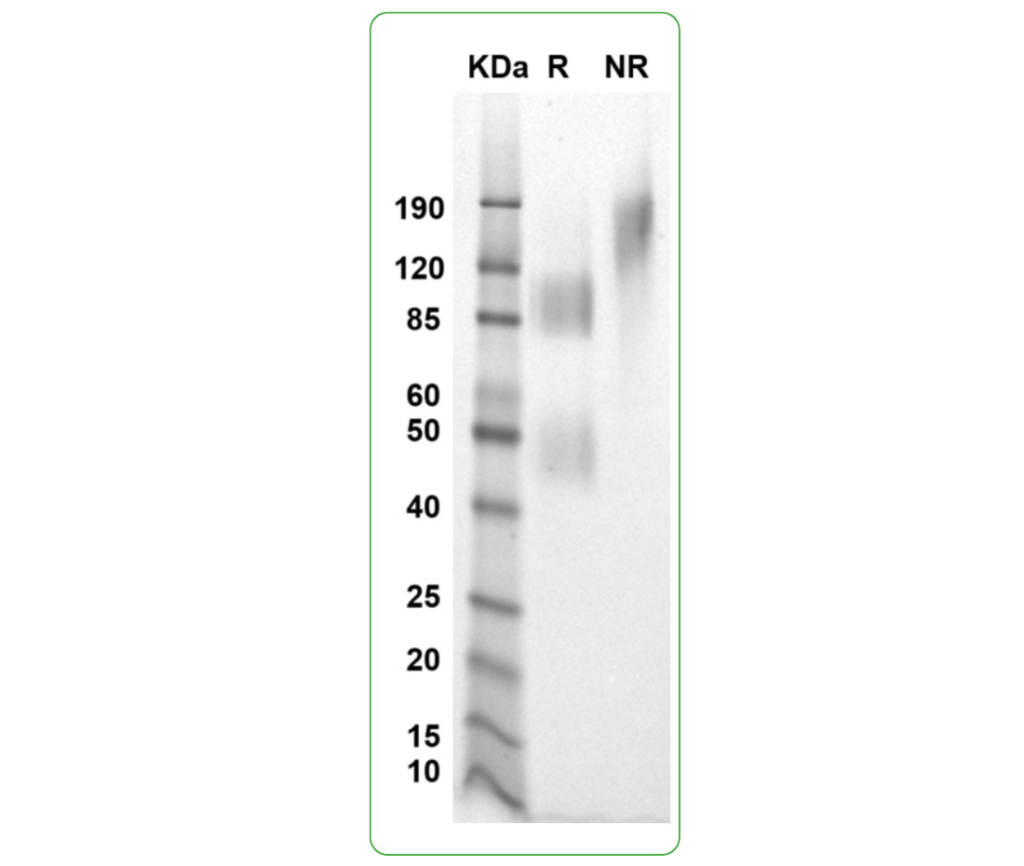
| Purity | Greater than 90% dimer form as determined by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing condition |
| Amino Acid Range | I27-K243 ; K28-K436 |
For Research Use Only (RUO)
Price: $125.00
Price: $195.00
Price: $350.00
Price: $1,050.00
Price: $3,500.00
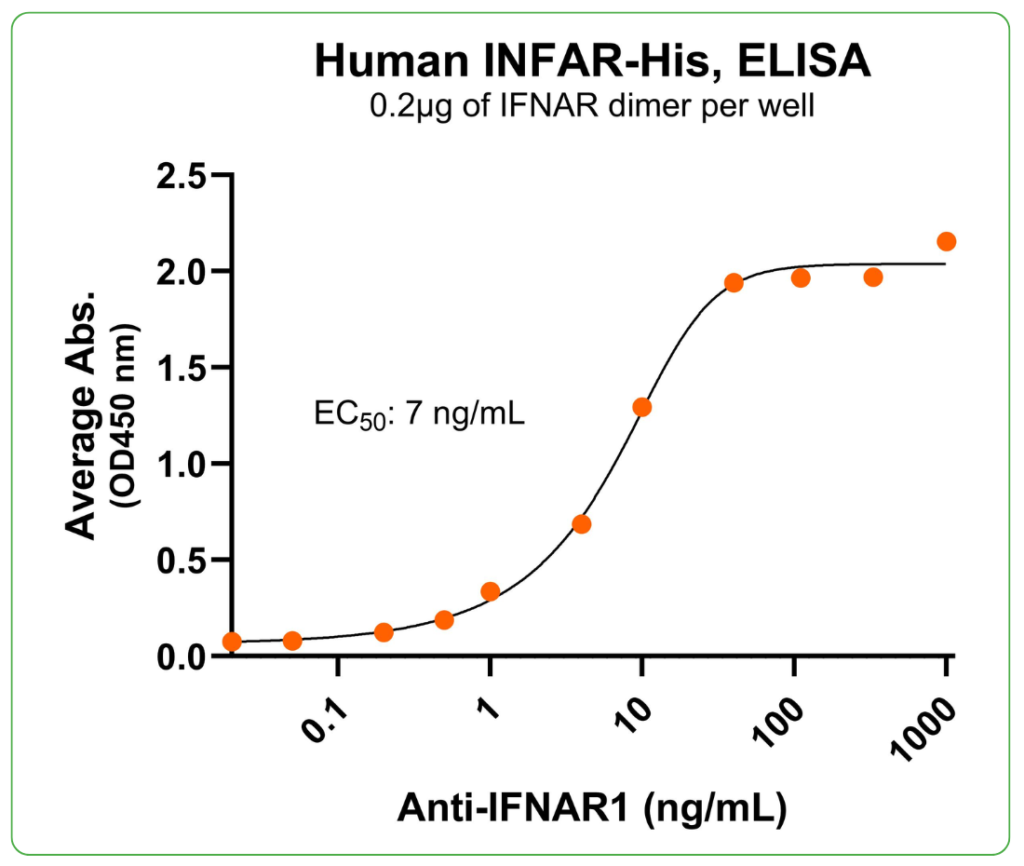
Bioactivity – Antibody Binding
Immobilized human IFNAR heterodimer protein, His Tag (Cat. No. CSP-24025-A1B1) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind anti-human INFAR1 monoclonal antibody with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 3.5-14 ng/mL (QC tested).
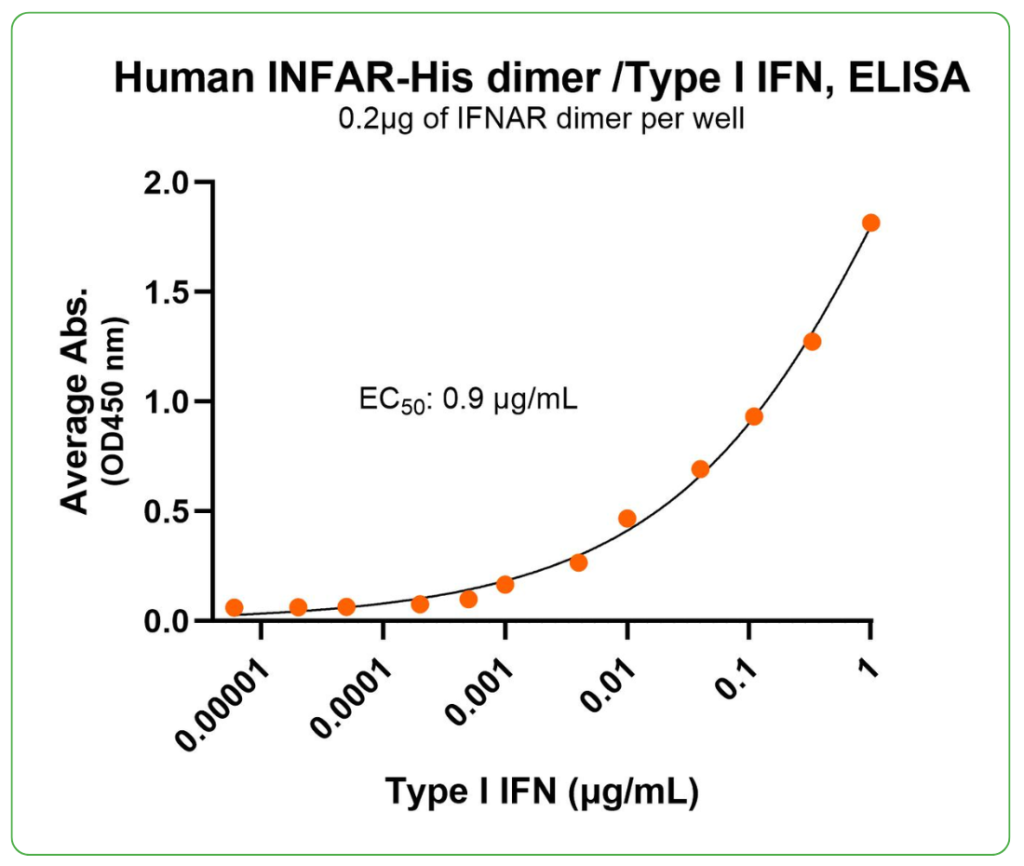
Bioactivity – Ligand Binding
Immobilized human IFNAR heterodimer protein, His Tag (Cat. No. CSP-24025-A1B1) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Type I Interferon cytokine with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 0.45-1.8 μg/mL (QC tested).
Specifications
Formulation: 0.22μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4
Shipping: Frozen Dry Ice
Storage: -80°C
Human IFNAR, also known as interferon-alpha/beta receptor, is a heterodimer complex comprised of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. Our recombinant human IFNAR (IFNAR1/R2) heterodimer protein (CSP- 24025) features the cis-heterodimer of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 with significantly enhanced binding potency to Type I interferons compared with each of the IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 monomers. The recombinant IFNAR1/R2 heterodimer protein (CSP- 24025) contains IFNAR1 (UniProt# P17181, amino acids Lys28-Lys436) and IFNAR2 extracellular domains (UniProt# P48551, amino acids Ile27-Lys243) fused with a proprietary dimer motif followed by a His tag at each C-terminus. This heterodimeric protein is expressed in HEK293T cells. The IFNAR heterodimer protein is bioactive and can bind to type I interferon (IFN) cytokines. It also binds IFNAR1 and IFNAR2-specific antibodies. This IFNAR heterodimer can be used as an antigen for in vitro assays and antibody screening, and as an immunogen for immunization to generate antibodies targeting more conformational epitopes.
Protein Name: IFNα-R1/R2
UniProt #: P17181 ; P48551
Predicted Molecular Weight: 87 kDa
SDS PAGE Molecular Weight: The migration range of the heterodimer under reducing conditions is 40-60 kDa and 70-120 kDa. The migration range of the heterodimer under non-reducing conditions is 120-190 kDa on SDS PAGE.
Protein Construct: IFNAR (IFNAR1/R2) heterodimer protein contains IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 extracellular domains (UniProt# P17181 and UniProt# P48551) fused with a proprietary dimer motif followed by a His tag at each C-termini.
Background
The interferon-alpha/beta receptor (interferon-α/β receptor, IFNAR, IFNaR, IFNαR), also known as Type 1 Interferon Receptor, is primarily located on the cell plasma membrane. IFNAR is a heterodimeric cell surface receptor complex composed of two subunits, IFNAR1 and IFNR2. Each subunit of IFNAR contains an N-terminal ligand binding domain containing two (IFNAR2) or four (IFNAR1) fibronectin type II-like subdomains, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 association is essential for recognizing type I interferon (IFN) cytokines such as IFN-α, IFN-β and others. The extracellular domains (ECDs) of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 are specifically responsible for binding Type 1 interferons. Type 1 interferon interaction with both IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 is essential for stabilizing the receptor-ligand binding and facilitating downstream signaling. Upon binding to type I IFNs, IFNAR activates the JAK-STAT, MAPK, PI3K, and Akt signaling pathways. As Type 1 interferon signaling plays important roles in immune responses, dysregulation of IFNAR activated pathways has been associated with various diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune disorders and cancer. IFNAR is an emerging therapeutic target for various types of diseases involving modulation of Type I interferon signaling. Our recombinant IFNAR1/R2 protein features the IFNAR heterodimer of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2.
Alternate Names: IFNAR1, IFNAR2, IFNAR, IFNaR, IFNAR1/R2, interferon-Alpha/Beta Receptor, interferon-α/β receptor