Bioactive, Human CD117 Dimer, His-Avi Tag
| Product Code | CSP-24123-03 |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Verified Applications | ELISA for CD117-specific antibody and stem cell factor (SCF) ligand protein binding assays. |
| Suggested Applications | ELISA for CD117-specific antibody and stem cell factor (SCF) ligand protein binding assays. SPR & BLI for CD117-specific antibody and stem cell factor (SCF) protein binding assays. Animal immunization, RUO. |
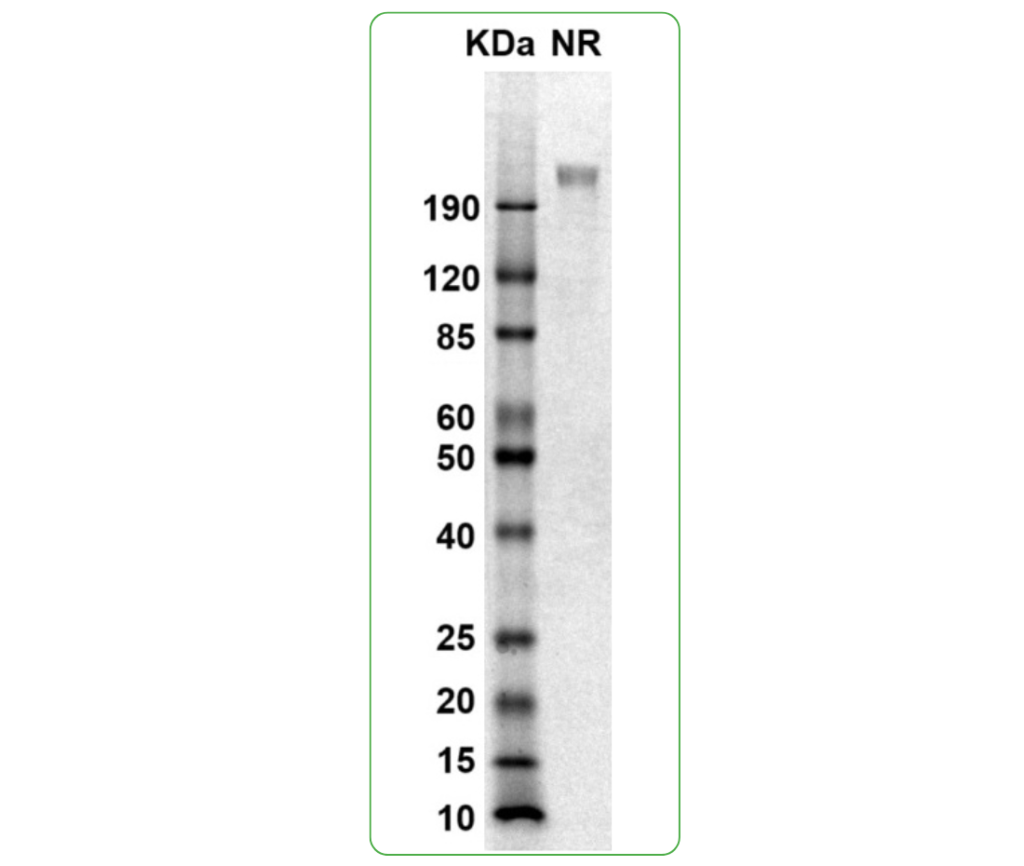
| Purity | Greater than 90% dimer form as determined by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing condition |
| Amino Acid Range | Ser25-Pro524 |
For Research Use Only (RUO)
Price: $125.00
Price: $195.00
Price: $350.00
Price: $750.00
Price: $2,500.00
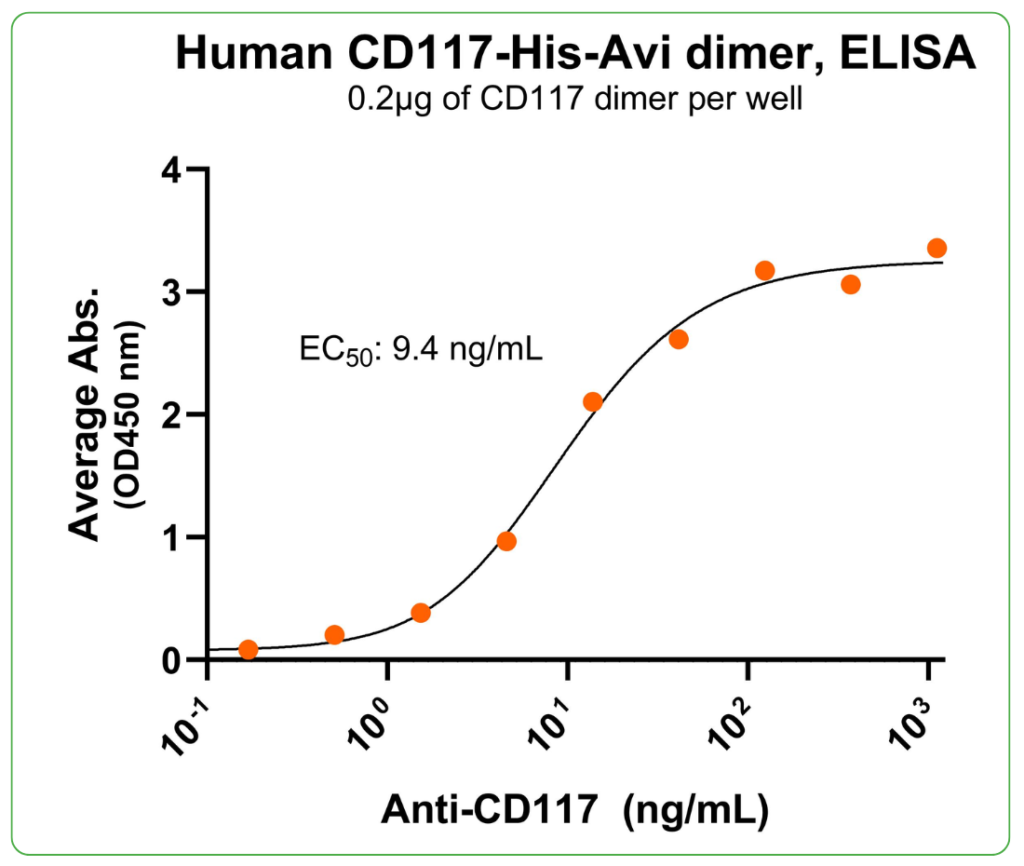
Bioactivity – Antibody Binding
Immobilized human CD117 dimer protein, His-Avi Tag (Cat. No. CSP-24123-03) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind anti-human CD117 monoclonal antibody, with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 4.7-18.8 ng/mL (QC tested).
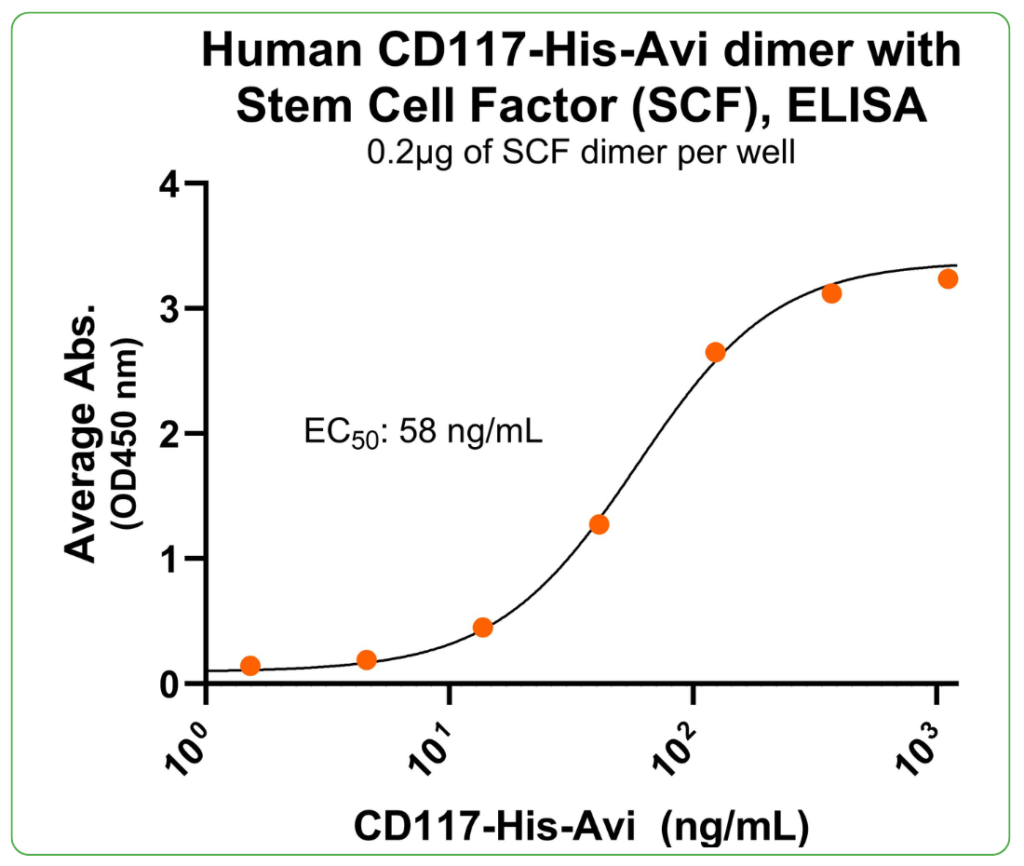
Bioactivity – Ligand Binding
Immobilized human Stem Cell Factor (SCF) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind human CD117 dimer protein, His-Avi Tag (Cat. No. CSP-24123-03), with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 29.1-116.4 ng/mL (QC tested).
Specifications
Formulation: 0.22μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4
Shipping: Frozen Dry Ice
Storage: -80°C
Human cluster of differentiation 117 (CD117), also known as KIT or c-Kit, is a member of the type III receptor tyrosine kinase family. The recombinant CD117 dimer protein (CSP-24123-03) is a cis-homodimer (cis-dimer) and contains a CD117 extracellular domain (UniProt# P10721, amino acids Ser25-Pro524) fused with a proprietary dimer motif followed by a tandem His-Avi tag at the C-terminus. This dimeric protein is expressed in HEK293 cells. The recombinant human CD117 dimer protein is bioactive and can bind to stem cell factor (SCF). It also binds CD117-specific antibodies. This CD117 dimer can be used as an antigen for in vitro assays and antibody screening, and as an immunogen for immunization to generate antibodies targeting more conformational epitopes.
Protein Name: CD117
UniProt #: P10721
Predicted Molecular Weight: 132 kDa
SDS PAGE Molecular Weight: The migration range of the dimer protein with glycosylation under non-reducing conditions is >190 kDa on SDS PAGE.
Protein Construct: CD117 dimer protein contains a CD117 extracellular domain (UniProt# P10721) fused with a proprietary dimer motif followed by a tandem His-Avi tag at the C-terminus.
Background
Human cluster of differentiation 117 (CD117), is a member of the type III receptor tyrosine kinase family. CD117 is also known as KIT, C-Kit, mast/stem cell growth factor receptor (SCFR), KIT proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase, and MASTC. CD117 contains an extracellular domain with five immunoglobulin-like loops, a transmembrane domain, a juxtamembrane domain, and an intracellular domain. CD117 is a type I transmembrane protein, expressed on hematopoietic stem cells, mast cells, melanocytes, germ cells, and interstitial cells of Cajal. CD117 exists as a monomer under normal physical conditions. Upon binding to its natural ligand, stem cell factor (SCF), homodimerization occurs between two CD117 monomers; this homodimerization is essential for its activation. However, oncogenic mutations can cause ligand-independent pathological dimerization and constitutive activation. CD117 is frequently overexpressed or dysregulated in cancers, including gastrointestinal stromal tumors, acute myeloid leukemia, melanoma, and small cell lung cancer. CD117 is a promising drug target, especially in precision oncology and regenerative medicine. Understanding CD117 dimerization and its activation is crucial for developing targeted therapeutics.
Alternate Names: KIT, C-Kit, cluster of differentiation 117, CD117, PBT, mast/stem cell growth factor receptor, SCFR, KIT proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase, MASTC